Dimensionality Reduction for Reacting Flows using Machine learning
Reacting flows are characterized by a multitude of interacting variables and scales, ranging from molecular-level reactions to macroscopic flow structures involving many chemical species. High-fidelity simulations, such as Direct Numerical Simulations (DNS), capture intricate spatiotemporal variations but are computationally expensive. Dimensionality reduction techniques can alleviate computational costs by learning a low-dimensional manifold and evolving the solution in that space with reasonable accuracy.
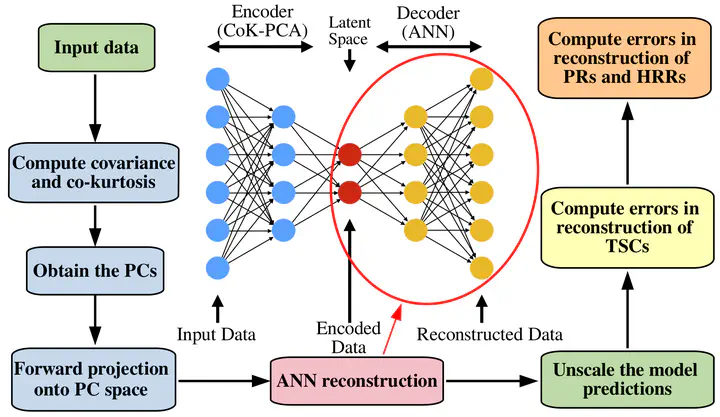
A turbulent flow is characterized by a wide range of spatial and temporal scales, and resolving these using Direct Numerical simulations is computationally expensive. In addition, in a reacting flow, a large number of governing equations must be solved to obtain the mass fractions of species, typically tens or hundreds, making it more challenging. Therefore, dimensionality reduction techniques are employed to reduce the number of equations that must be solved. The motivation behind this is that the mass fractions of various species are highly correlated and a low-dimensional manifold may be found which captures the state of chemical reactions reasonably well. In this regard, we propose a method known as co-kurtosis PCA which is based on fourth-order joint statistical moments and has been found to capture the reaction dynamics better than the traditionally employed PCA. To reconstruct the thermo-chemical scalars from the principal components and model the closure terms in the PC transport equation, we use a fully connected neural network. In a recent work, to further improve the accuracy of the predictions for the case of autoignition in a homogenous reactor, we employ Neural Ordinary Differential equations (Neural ODE) and found them to be more accurate than the traditional method of training the neural network for the closure term.
Publications:
- Nayak, D., Jonnalagadda, A., Balakrishnan, U., Kolla, H., & Aditya, K. (2024). A co-kurtosis PCA based dimensionality reduction with nonlinear reconstruction using neural networks. Combustion and Flame, 259, 113192.
- Jonnalagadda, A., Kulkarni, S., Rodhiya, A., Kolla, H., & Aditya, K. (2023). A co-kurtosis based dimensionality reduction method for combustion datasets. Combustion and Flame, 250, 112635.